Determine the pH in a 0.667 M NaOH solution.
Group of answer choices0.12
0.18
14.18
13.88
13.82
Question 22 pts
What is the pH of a buffer solution that is 0.192 M in lactic acid and 0.155 M in sodium lactate? The Ka of lactic acid is 1.4 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices3.94
14.09
10.24
3.76
5.48
Question 32 pts
Determine the pH of a 0.22 M NaF solution at 25°C. The Ka of HF is 3.5 × 10-5.
Group of answer choices5.10
11.44
10.20
8.90
2.56
Question 42 pts
Which of the following compounds solubility will NOT be affected by a low pH in solution?
Group of answer choicesBaCO3
AgCl
CuS
Mg(OH)2
BaF2
Question 52 pts
Determine the molar solubility of CaSO4 in a solution containing 0.060 M Na2SO4. Ksp (CaSO4) = 2.4 × 10-5.
Group of answer choices5.8 × 10-10 M
4.0 × 10-4 M
0.30 M
1.4 × 10-6 M
4.9 × 10-3 M
Question 62 pts
Calculate the pH for an aqueous solution of pyridine that contains
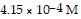
hydroxide ion.
Group of answer choices4.15 × 10-4
7.05
2.41 × 10-11
10.62
3.38
Question 72 pts
Identify the base that is in baking soda.
Group of answer choicesNaHCO3
LiOH
KHCO3
RbOH
Li2CO3
Question 82 pts
A 25.0 mL sample of 0.150 M butanoic acid is titrated with a 0.150 M NaOH solution. What is the pH at the equivalence point? The Ka of butanoic acid is 1.5 × 10-5.
Group of answer choices8.85
11.82
9.18
7.10
4.82
Question 92 pts
Determine the [H3O+] concentration for a 0.200 M solution of HCl.
Group of answer choices1.00 × 10-1 M
4.00 × 10-1 M
2.50 × 10 -14 M
1.25 × 10-14 M
2.00 × 10-1 M
Flag question: Question 10Question 102 pts
A ligand is a molecule or ion that acts as a
Group of answer choicesLewis base.
Brønsted-Lowry base.
conjugate acid.
Arrhenius base.
Lewis acid.
Flag question: Question 11Question 112 pts
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.112 M in sodium formate (NaHCO2) and
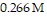
in formic acid

The Ka of formic acid is 1.77 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices10.63
5.073
3.369
14.38
4.121
Flag question: Question 12Question 122 pts
A 700.0 mL sample of 0.18 M HClO4 is titrated with 0.27 M CsOH. Determine the pH of the solution after the addition of 350.0 mL of CsOH.
Group of answer choices1.52
0.68
2.35
12.48
3.22
Flag question: Question 13Question 132 pts
What is the pH of a 0.020 M Ba(OH)2 solution?
Group of answer choices1.70
1.40
12.60
13.20
12.30
Flag question: Question 14Question 142 pts
A solution contains Fe2+, Ba2+, Ag+, NH4+, and Cd2+. Identify the soluble compound after the addition of 6 M HCl; then H2S and 0.2 M HCl; then OH- to a pH of 8; and then (NH4)2HPO4 with NH3.
Group of answer choicesBa3(PO4)2
CdS
NH4Cl
FeS
AgCl
Flag question: Question 15Question 152 pts
Which of the following is a Lewis acid?
Group of answer choicesAlBr3
CHBr3
NH3
CCl4
None of the above is a Lewis acid.
Flag question: Question 16Question 162 pts
Calculate the Ksp for hydroxide if the solubility of Mn(OH)2 in pure water is 7.18 × 10-1 g/L.
Group of answer choices2.10 × 10-6
5.50 × 10-11
8.07 × 10-3
7.18 × 10-1
5.25 × 10-7
Flag question: Question 17Question 172 pts
What is the hydronium ion concentration of a 0.100 M hypochlorous acid solution with
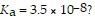
The equation for the dissociation of hypochlorous acid is:
HOCl(
aq) + H2O(
l) ⇌ H3O+(
aq) + OCl-(
aq)
Group of answer choices5.9 × 10-4 M
1.9 × 10-5 M
1.9 × 10-4 M
5.9 × 10-5 M
Flag question: Question 18Question 182 pts
What is the pH of a solution made by mixing 29.00 mL of 0.10 M acetic acid with 29.00 mL of 0.10 M KOH? Assume that the volumes of the solutions are additive. Ka =
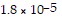
for CH3CO2H.
Group of answer choices7.00
5.28
6.22
10.02
8.72
Flag question: Question 19Question 192 pts
Calculate the pH of a solution formed by mixing 150.0 mL of 0.20 M HClO with 300.0 mL of 0.30 M CsClO. The Ka for HClO is 2.9 × 10-8.
Group of answer choices6.46
5.99
7.06
7.54
8.01
Flag question: Question 20Question 202 pts
Calculate the pH of a 0.16 M carbonic acid solution, H2CO3(
aq), that has the stepwise dissociation constants
Ka1 = 4.3 × 10-7 and
Ka2 = 5.6 × 10-11.
Group of answer choices3.58
10.25
6.37
0.80
Flag question: Question 21Question 212 pts
What is the hydroxide ion concentration of a NaOH solution that has a pH of 12.20?
Group of answer choices12.20 M
1.58 × 10-2 M
1.80 M
7.20
6.31 × 10-13 M
Flag question: Question 22Question 222 pts
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 0.322 M in nitrous acid (HNO2) and 0.178 M in potassium nitrite (KNO2). The acid dissociation constant of nitrous acid is 4.50 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices3.607
10.91
4.554
14.26
3.093
Flag question: Question 23Question 232 pts
What is the pH of the resulting solution if 45.00 mL of 0.10 M acetic acid is added to 10.00 mL of 0.10 M KOH? Assume that the volumes of the solutions are additive. Ka = 1.8 × 10-5 for CH3CO2H

Group of answer choices6.62
5.29
9.80
4.20
8.71
Flag question: Question 24Question 242 pts
Place the following in order of
increasing acid strength.
HBrO2HBrO3HBrOHBrO4
Group of answer choicesHBrO4 < HBrO2 < HBrO3 < HBrO
HBrO < HBrO4 < HBrO3 < HBrO2
HBrO2 < HBrO4 < HBrO < HBrO3
HBrO < HBrO2 < HBrO3 < HBrO4
HBrO2 < HBrO3 < HBrO4 < HBrO
Flag question: Question 25Question 252 pts
Determine the pH of a 0.00444 M HClO4 solution.
Group of answer choices1.353
2.353
12.647
11.647
5.824
Flag question: Question 26Question 262 pts
A 6.0 × 10-3 M aqueous solution of Ca(OH)2 at 25.0°C has a pH of ________.
Group of answer choices5.6 × 10-13
12.08
1.92
11.78
1.2 × 10-2
Flag question: Question 27Question 272 pts
An aqueous solution at 25.0°C contains [H+] = 0.099 M. What is the pH of the solution?
Group of answer choices0.0990
1.00
13.0
-1.00
1.20 × 10-13
Flag question: Question 28Question 282 pts
Calculate the molar solubility of thallium chloride in 0.0.25 M NaCl at 25°C. Ksp for TlCl is
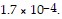
Group of answer choices8.2 × 10-3 M
6.8 × 10-4 M
1.7 × 10-5 M
1.3 × 10-2 M
Flag question: Question 29Question 292 pts
Calculate the pH for an aqueous hydroiodic acid solution that contains
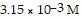
hydronium ion.
Group of answer choices11.50
2.50
12.50
3.17 × 10-12
3.15 × 10-3
Flag question: Question 30Question 302 pts
Describe what happens at high pH for aluminum hydroxide.
Group of answer choicesAl(H2O)23+ precipitates.
Al precipitates.
Al dissolves.
Al(H2O)2(OH)4- dissolves.
Al(OH)5 precipitates.
Flag question: Question 31Question 312 pts
Which of the following acids (listed with Ka values) and their conjugate base should be used to form a buffer with a pH of 2.34?
Group of answer choicesHClO2, Ka = 1.1 × 10-2
HIO, Ka = 2.3 × 10-10
HCN, Ka = 4.9 × 10-10
C6H5OH, Ka = 1.3 × 10-10
HN3, Ka = 2.5 × 10-5
Flag question: Question 32Question 322 pts
How many milliliters of 0.0991 M LiOH are required to titrate 25.0 mL of
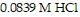
to the equivalence point?
Group of answer choices0.208
4.58
29.5
21.2
0.333
Flag question: Question 33Question 332 pts
A solution contains Ba2+, Hg2+, Ag+, NH4+, and Fe2+. Identify the precipitate after the addition of 6 M HCl.
Group of answer choicesHgS
Ba3(PO4)2
FeS
AgCl
NH4Cl
Flag question: Question 34Question 342 pts
Identify the diprotic acid.
Group of answer choicesCH3COOH
HNO3
H2SO3
HClO4
HF
Flag question: Question 35Question 352 pts
Find the percent ionization of a 0.337 M HF solution. The Ka for HF is 3.5 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices4.7%
1.2 × 10-2%
3.2%
1.1%
3.5 × 10-2%
Flag question: Question 36Question 362 pts
Identify the
weak monoprotic acid.
Group of answer choicesH2CO3
NaBr
HF
HNO3
LiOH
Flag question: Question 37Question 372 pts
Determine the pH of a 0.141 M RbOH solution at 25°C.
Group of answer choices13.86
13.15
0.141
0.851
0.88
Flag question: Question 38Question 382 pts
Calculate the pH of a solution that contains 7.8 × 10-6 M OH⁻ at 25°C.
Group of answer choices8.89
12.72
1.28
5.11
9.64
Flag question: Question 39Question 392 pts
What is the pH of a 0.300 M NH3 solution that has
Kb = 1.8 × 10-5? The equation for the dissociation of NH3 is:
NH3(
aq) + H2O(
l) ⇌ NH4+(
aq) + OH-(
aq)
Group of answer choices10.89
2.11
11.37
6.22
2.63
Flag question: Question 40Question 402 pts
A 150.0 mL sample of 0.18 M HClO4 is titrated with 0.27 M LiOH. Determine the pH of the solution after the addition of 45.0 mL of LiOH.
Group of answer choices1.21
1.12
0.86
2.00
2.86
Flag question: Question 41Question 412 pts
Formic acid (HCO2H, Ka = 1.8 × 10-4) is the principal component in the venom of stinging ants. What is the molarity of a formic acid solution if 25.00 mL of the formic acid solution requires 74.80 mL of 0.0567 M NaOH to reach the equivalence point?
Group of answer choices0.170 M
0.0375 M
0.0190 M
0.0567 M
0.0134 M
Flag question: Question 42Question 422 pts
Which of the following acids (listed with pKa values) and their conjugate base should be used to form a buffer with a pH of 8.10?
Group of answer choicesHC7H5O2, pKa = 4.19
HF, pKa = 3.46
HClO, pKa = 7.54
H2SO3, pKa = 1.77
HClO2, pKa = 1.96
Flag question: Question 43Question 432 pts
Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 1.26 M HClO and 0.079 M NaClO. The Ka for HClO is 2.9 × 10-8.
Group of answer choices7.46
6.67
7.74
7.54
6.34
Flag question: Question 44Question 442 pts
A 550.0 mL sample of 0.18 M HClO4 is titrated with 0.27 M KOH. Determine the pH of the solution after the addition of 550.0 mL of KOH.
Group of answer choices1.35
12.85
12.65
13.13
0.87
Flag question: Question 45Question 452 pts
Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.080 M HF and 0.040 M NaF. The Ka for HF is 3.5 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices4.86
2.06
3.56
3.76
3.16
Flag question: Question 46Question 462 pts
Which one of the following salts, when dissolved in water, produces the solution with the
highest pH?
Group of answer choicesCsCl
CsI
CsF
CsBr
Flag question: Question 47Question 472 pts
What is the pH at the equivalence point of a weak base-strong acid titration if 20.00 mL of NaOCl requires 28.30 mL of 0.40 M HCl to reach the equivalence point? Ka = 3.0 × 10-8 for HOCl.
Group of answer choices2.10
0.40
3.23
3.76
4.08
Flag question: Question 48Question 482 pts
A solution contains Zn2+, Hg2+, Ag+, NH4+, and Ba2+. Identify the precipitate after the addition of 6 M HCl, then H2S and 0.2 M HCl.
Group of answer choicesBa3(PO4)2
ZnS
NH4Br
AgCl
HgS
Flag question: Question 49Question 492 pts
A 220.0 mL sample of 0.20 M HF is titrated with 0.10 M NaOH. Determine the pH of the solution after the addition of 440.0 mL of NaOH. The Ka of HF is 3.5 × 10-4.
Group of answer choices3.46
8.14
7.00
9.62
10.54
Flag question: Question 50Question 502 pts
The
largest change in pH for an effective buffer occurs when the base is how many times as concentrated as the acid?
Group of answer choices6
20
5
40
10